EV charging technology is categorized into three charger levels, each with varying charging speeds and applications.
Level 1 chargers utilize standard 120 volt wall outlets, providing a slow charge that is ideal for overnight use at home. These chargers are often included when you purchase an electric vehicle, but can also be purchased at third-party retailers for a few hundred dollars.
Level 2 chargers, or wallbox chargers, operate from 208 or 240 volt outlets, like many home appliances. They are capable of delivering a full charge to most electric vehicles within a few hours, making this technology suitable for in-home use and commercial EV charging stations.
Level 3 chargers, also known as DC fast charging stations, operate on 480 volts and have the capability to replenish up to 80% of a battery’s power in as little as 20 to 30 minutes. This convenience renders them perfect for areas with a high volume of traffic.
Each power level is designed to meet distinct charging needs in various situations, but the difference goes beyond their utilization.
AC vs DC Power
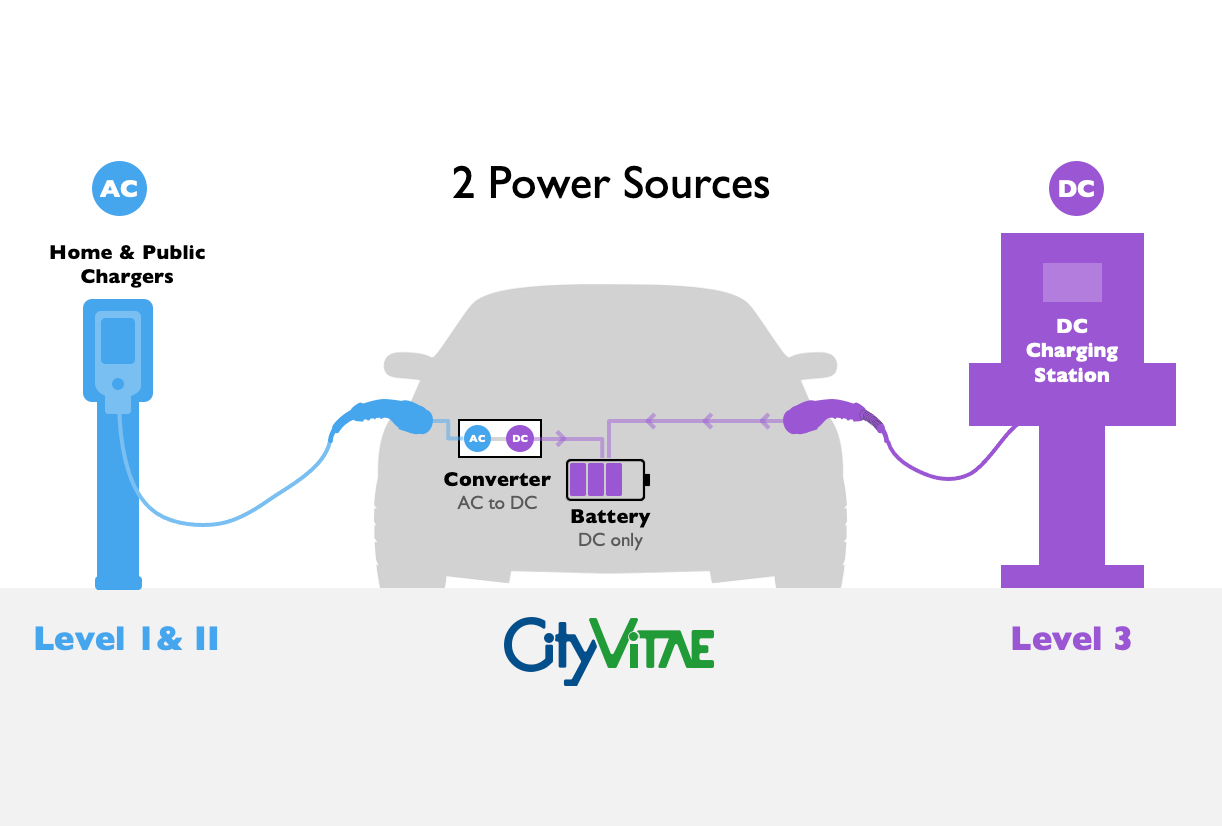
Alternate current (AC) power is used by level 1 and level 2 charging stations, while level 3 chargers use direct current (DC).
Imagine electricity as a river. With DC power, the electricity flows in one direction continuously, similar to a river running from the mountains toward the sea. For DC charging stations, this means the electricity is going straight from your charger to your electric vehicle’s battery, with nothing in between.
The electricity that we typically use for home electronics and appliances is different. This is called AC power, where the flow of electricity alternates or changes direction. Imagine the water in the river flowing in two directions at the same time.
Because batteries can only store DC power, the AC power coming from the electric network needs to be converted into direct current through a transformer. Level 3 charging stations have this transformer built into the charging unit itself, while level 1 and 2 EV chargers utilize a transformer within the car.
A level 3 charger provides power that’s already in the correct, one-way flow, eliminating the need for conversion inside the vehicle. This is why DC charging stations will charge electric car much faster!
What To Look Out For
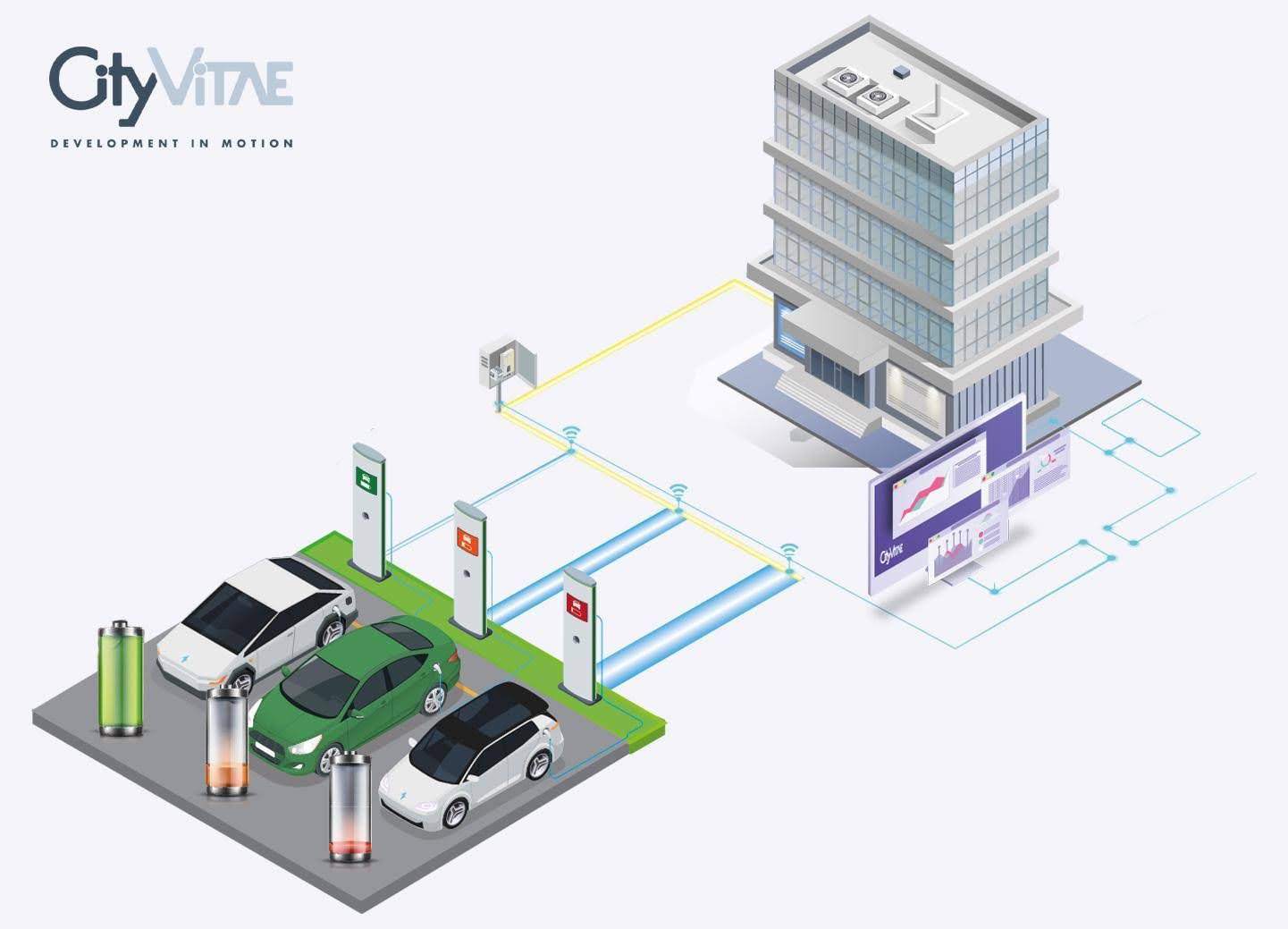
- Software developed in-house
- A charging station app for users
- Dynamic pricing – being able to set different rates at different times
- Remote monitoring of the charging system
- Revenue management system
- Dynamic charging – the system is able to expand beyond the electrical capacity of the property by using powerful IT software, e.g. being able to charge 20 cars simultaneously when there is only capacity for 5
Executive Summary
When looking to install EV chargers, you need to look for a company that offers a system-wide solution, including the charger, the app, the software, and the electrical infrastructure. That way you are able to take action in the short term while laying the groundwork for the long term.
EV charging station prices can be anywhere from $3000-20,000 depending on the level, and EV charger installation can be between $5000-7000 depending on existing electrical infrastructure.
Want to learn more about the optimal EV charging needs for your business and property?
Call CityVitae today for a free on-site evaluation and we’ll advise you regarding your electrical capacity, what kind of chargers to install, how many chargers to install, and the installation cost.
Let us help you navigate the exciting, electrifying road ahead!